"...Αγαπητέ
Γιάννη, για την πρώτη και δεύτερη ουσία
στον Αριστοτέλη στα έργα του: α) Κατηγορίαι
2a, 2b. β) Μετά
τα Φυσικά Ζ3...''
Παρασκευή 19 Ιουλίου 2019
Τρίτη 11 Ιουνίου 2019
Σάββατο 8 Ιουνίου 2019
Παρασκευή 31 Μαΐου 2019
Σοσιαλιστική δημοκρατία και έριδα..
Υπάρχουν διάφορες προσπάθειες για την καταγωγική θεμελίωση τής έννοιας τής δημοκρατίας, και δεν προτίθεμαι βέβαια να τις παραθέσω τώρα, αλλά μπορώ να σας δώσω ένα μεζεδάκι για το πως θεωρώ εγώ ότι μπορεί να οριστεί μια νέα σοσιαλιστική μορφή της χωρίς να δεσμεύεται απόλυτα από την οποιαδήποτε καταγωγική θεμελίωση:
Βασικό στοιχείο των ανταγωνιστικών ταξικών κοινωνιών είναι η έριδα και η αγεφύρωτη σύγκρουση μεταξύ ατόμων, κοινωνικών τάξεων και μεταξύ άλλων κοινωνικών ή "ιδεολογικών" ομάδων.
Δεν θεωρώ ότι στον σοσιαλισμό που επιθυμώ θα εκλείψουν οι σκληρές αντιθέσεις, άρα και οι αντιπαραθέσεις μεταξύ ατόμων και κοινωνικών ομάδων, αν και οφείλω να "ξεκαθαρίσω" ότι για μένα δεν νοείται σοσιαλισμός χωρίς να υπάρχει δια αυτού κατάργηση των σχέσεων οικονομικής εκμετάλλευσης και καταπίεσης, χωρίς δηλαδή να υπάρξει κατάργηση τής ύπαρξης μιας ξεχωριστής τάξης ιδιοκτητών των [βασικών] μέσων παραγωγής και των πόρων.
Θα υπάρχουν άλλοι λόγοι σύγκρουσης και αντιπαράθεσης, θα υπάρχουν διαφορετικές γνώμες, διαφορετικές στρατηγικές για την πολιτική, οικονομική ίσως και πολιτισμική "υφή" του σοσιαλισμού.
Δεν θεωρώ ότι αυτοί οι ανταγωνισμοί θα είναι ήπιοι, όπως επίσης δεν θεωρώ ότι υπάρχει κάποια οντολογική διασφάλιση ότι οι συγκρούσεις που θα προκύπτουν από τις αντίθετες στάσεις και γνώμες θα είναι εύκολα αφομοιώσιμες σε ένα εκ των προτέρων διασφαλισμένο ως μη-ανταγωνιστικό κοινωνικό συνεχές.
Απλά το κοινό υπόβαθρο των συγκρούσεων θα είναι διαφορετικό από το κοινό υπόβαθρο στο οποίο έχουμε συνηθίσει να ζούμε ζώντας σε μια ταξική καταπιεστική κοινωνία όπου μια οικονομική ολιγαρχία "κανονίζει" την κοινωνική κανονικότητα σύμφωνα με τα οικεία ιδιοτελή συμφέροντα της και όπου τα υπόλοιπα "μέλη" τής κοινωνίας είναι "αναγκασμένα" να αγωνίζονται συνέχεια, υπό ανταγωνιστικούς όρους, για την ίδια την επιβίωση και αυτοσυντήρηση τους.
Η δημοκρατική απάλειψη των καταπιεστικών εκμεταλλευτικών όρων τής κοινωνικής παραγωγής, εν συντομία η υπέρβαση τού καπιταλιστικού αλλά και του κρατικιστικού τρόπου παραγωγής, θεωρώ όμως ότι θα φέρει ένα είδος δημοκρατικής ειρήνευσης, χωρίς να σημαίνει κατάργηση κάθε είδους ανταγωνισμού και σύγκρουσης.
Οι ποικίλες διατομικές και κοινωνικές συγκρούσεις θα συνεχίζονται σε ένα άλλο πλαίσιο, αλλά νομίζω ότι εντός τής σοσιαλιστικής δημοκρατίας θα εκλείψει η ακρότητα αυτών των συγκρούσεων, η αβυσσαλέα έκρηξή τους όπως λόγου χάριν παράγεται αναπόφευκτα από το ακραίο υλικό πλαίσιο ζωής των εργαζόμενων πολιτών μιας σύγχρονης καπιταλιστικής δημοκρατίας.
Η εικόνα ενός τέτοιου είδους σοσιαλιστικού δημοκρατισμού μάς ωθεί ή πρέπει να μας ωθήσει να αναθεωρήσουμε την μορφή και το περιεχόμενο τού μέχρι τώρα επαναστατισμού ή δημοκρατισμού μας, σε σχέση μάλιστα με όσα είπαμε στην αρχή.
Οι δημοκρατίες των ταξικών κοινωνιών [όταν υπήρξανε ή όπως υπάρχουν] δεν παύουν να είναι δημοκρατίες, δεν θεωρώ άρα ότι υπάρχει μια εντελώς "μη καταγωγική" θεμελίωση των σοσιαλιστικών δημοκρατικών προτύπων μας, αλλά ταυτόχρονα η δημοκρατία που θέλουμε να υπάρξει ως εργατική δημοκρατία πρέπει να κομίζει ένα νέο ιδιαίτερο στοιχείο που αφορά σε αυτήν την νέα μη-εριστική ή μη-απόλυτα εριστική και μη-δικηγορίστικη έκφραση και ουσία της.
Μέχρι τώρα ο δημοκρατισμός των εργαζόμενων πολιτών πιθήκιζε τον δημοκρατικό Λόγο των ρητόρων-δικηγόρων των ταξικών και ενδοταξικών συγκρούσεων των ταξικών δημοκρατιών, όπως διαμορφώνονταν και διαμορφώνεται [ως Λόγος] μέσα σε ένα πραγματικό ή φαντασιακό πεδίο μιας πραγματικής ή φαντασιακής ιστορικής δίκης.
Η έριδα και η εριστικότητα παρουσιάζονταν ως ο μοναδικός τρόπος τής δημοκρατικής σοφιστικής.
Τίποτα από όλα αυτά δεν πρόκειται να εκλείψει, οι αντιθέσεις και οι συγκρούσεις δεν θα λείψουν, αλλά υπάρχει ωστόσο ανάγκη να ανακαλύψουμε [πέραν των αστικών ή μικροαστικών "ευγενειών"] την ευγένεια τού σοσιαλιστικού ήθους, όπως τούτο θα προκύπτει [και] από τις συνεργατικές και συντροφικές σοσιαλιστικές παραγωγικές σχέσεις.
Ιωάννης Τζανάκος
Πέμπτη 23 Μαΐου 2019
Ibrahim Kaypakkaya on the Kurdish National Question
Πηγή: dazibao rojo
Ibrahim Kaypakkaya on the Kurdish National Question
The following text is excerpted from a lengthy polemic by Ibrahim Kaypakkaya entitled The National Question in Turkey. This work was originally completed in December 1971, before Ibrahim Kaypakkaya led the genuine Marxist-Leninists in splitting with the Shafak revisionists, who were also
The
excerpts printed here are translated from a collection entitled
Selected Writings, Ibrahim Kaypakkaya, which was published by Ocak
Yayinlari, Istanbul, 1979. AWTW
2. Who is subjected to national oppression?
According
to the Shafak revisionists, it is the Kurdish people who
are being subjected to national oppression. This fails to grasp
what national oppression means. National oppression is the oppression
to which the ruling classes of the dominant nation subject the oppressed,
dependent and minority nations. In Turkey, national oppression is
the oppression by the ruling classes of the dominant Turkish nation
not just of the Kurdish people but of the entire Kurdish nation,
and not even of the Kurdish nation alone, but of all minority
nationalities.
Who is Ibrahim Kaypakkaya?
Πηγή:
Ibrahim Kaypakkaya – Selected Works
Who is Ibrahim Kaypakkaya?
İbrahim Kaypakkaya (1949 – May 18, 1973) was a major leader of the Communist movement in Turkey. He was the founder of the Communist Party of Turkey/Marxist-Leninist (TKP/ML).
Following the military memorandum of 1971,
the Turkish government cracked down on the Communist movement in Turkey
and was successful in destroying the machinery of the TKP/ML.
Kaypakkaya and several of his colleagues were arrested. Kaypakkaya died
in prison in 1973 after being tortured for over 4 months and later being
shot in the head by his interrogators.
He
is revered by his admirers today as a symbol of resistance, who
describe him as an aggregator of the ideas and traits of other major
leaders and thinkers in Marxism-Leninism-Maoism.
Σάββατο 18 Μαΐου 2019
How did the Iranian Revolution go so far off the rails? – People's World
Πηγή:
How did the Iranian Revolution go so far off the rails? – People's World
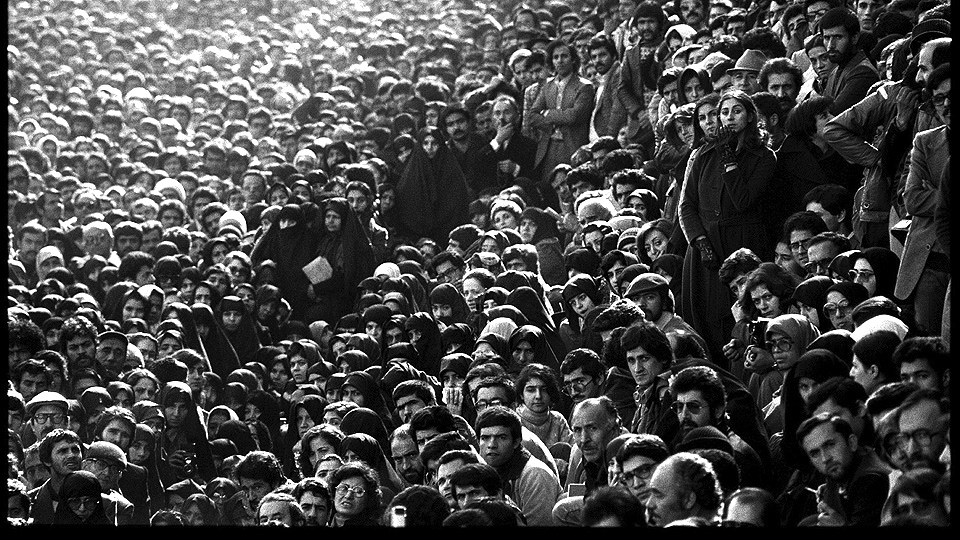

The Iranian Revolution was supported by millions of people from all walks of life. | Courtesy Tudeh Party of Iran
Even though it has to wage much of its struggle underground, the Tudeh Party of Iran, 40 years after the overthrow of the autocratic U.S.-installed Shah, continues the fight for a secular, democratic, and socialist Iran. The following is an exclusive interview with Mohammad Omidvar, a member of the political bureau of the Tudeh Party.
Since left and progressive forces, including labor unions, wage
an underground struggle in Iran, special measures had to be taken to
conduct this interview. The questions and the answers were transmitted
to and from Iran by a People’s World source outside that country. The
Tudeh Party chose People’s World as the venue for this important
interview because it wanted to give people in our country, on the 40th
anniversary of the Iranian Revolution, a better understanding of what is
happening in Iran.
The movement that started out with great hope for the future of
that country became, for many reasons, a failed revolution. This
interview helps clarify for our readers the reasons for this failure and
outlines the direction in which the progressive forces in Iran hope to
lead their country now. Omidvar also explains why the Tudeh Party
opposes current U.S. sanctions against Iran and why the Trump policy of
regime change is so fiercely opposed by the country’s progressive
forces.
– John Wojcik, editor-in-chief, People’s World
People’s World:
Progressive forces around the world had assessed the February 1979
revolution in Iran as a broadly-supported, all-encompassing social
revolution, one of the most exciting and popular uprisings of the 20th
century. What were the key factors in the final years of the Shah’s rule
that led to the revolution? Iran under the Shah was often represented
in the Western media as a strong, modern, and even democratic country.
Was this the case?
Mohammad Omidvar—The 1979 revolution in Iran was a national
democratic revolution, a classic example of a majority- supported
revolution that took place in the particular circumstances of the growth
of capitalism in Iran. In the 1960s and ’70s, Iranian society faced a
profound structural crisis due to the expansion of capitalist
relations whereby representatives of the comprador bourgeois class
dominated the political and economic life of the country.
The ever-increasing influence of capital in the Iranian economy, with
a police state that prevailed to safeguard the despotic client
regime, resulted in the middle strata becoming ever more squeezed. This
also led to the weakening of the economic positions of sections of the
national bourgeoisie. It is also noteworthy that during the same period
the working class was experiencing a modest growth due to the migration
of a large number of people from rural areas into cities as a result of
the pseudo-land reforms enacted. The real reason for these limited
reforms was to eliminate the threat to the Shah’s regime from large
landowners.
This gave the growing working class more social weight within the
class structure of our society. The 1979 Revolution, therefore, arose
from serious socio-economic crises and class contradictions
created by the dominating interests of comprador bourgeois and the
despotic rule of a corrupt, pro-western regime. It mobilized millions of
people—from workers, peasants, and the petty bourgeoisie to sections of
the small and medium national bourgeoisie—against the Shah’s regime.
The Iranian Revolution and the toppling of the Shah’s
regime was supported by the vast majority of people; millions were in
the streets calling for change. What were the key demands of the
majority of these forces in the 1979 Revolution, and was the
establishment of a theocratic state one of them?
As mentioned before, a wide range of social forces—from the working
class to the national bourgeoisie, the middle strata, and the petty
bourgeoisie, and the various socio-political forces representing their
interests—participated in the revolution with different perspectives and
programs. The people’s slogan was “Freedom, Independence, and Social
Justice,” and that was the approach supported by our party. The
religious forces insisted on adding the “Islamic Republic” to the
people’s demands; they did not reveal, at first, what that would mean in
practice. They revealed nothing of the characteristics of the kind of
state they were planning.
How and why did the forces of what you describe as
“political Islam” manage to gain the upper hand? Wasn’t it possible for
other revolutionary and/or secular forces to prevent this?

The ruling theocratic regime’s propaganda claims that the people of
Iran came to the streets to topple the regime of the Shah in order to
establish the “rule of Islam.” In reality, the 1979 Revolution had a
clear social and class context that was aimed at removing the
destructive influence of imperialist monopolies from our country,
securing Iran’s economic and political independence, establishing
justice, and democratizing the political and cultural life of our
society.
The 1979 Revolution ended up being taken over by religious forces for
a number of critical reasons, dating right back to the aftermath of the
1953 CIA-MI6 coup d’état in Iran, which re-established the Shah’s
regime. Over the following 25 years, while the left forces—especially
the Tudeh Party of Iran, the nationalist forces and, later on, the
guerrilla movements, including the People’s Fedaian and People’s
Mujahedin—were heavily suppressed by the security forces, the clergy
were allowed to use their networks, mosques, and religious events to
organize and promote their agenda (Political Islam).
The Shah’s regime and its dreaded security force, SAVAK, saw the
clergy as an important tool in countering the left and radical forces in
Iran. Indeed, in letters exchanged between then-President Carter and
Ayatollah Khomeini (now published in the mémoires of Dr. Yazdi,
Khomeini’s close confidante in Paris and Iran’s first post-revolutionary
foreign minister), the U.S. was prepared to tolerate Khomeini’s regime
provided they guaranteed to stop the influence of the Tudeh Party of
Iran in Iran’s post-revolution era.
In your publications, your assessment is that, after its
initial success in overthrowing the Shah’s regime and bringing about a
number of political changes, the 1979 Revolution was halted and
ultimately failed. What characterizes it as a failed revolution, and was
this inevitable? Could other revolutionary forces, including the Tudeh
Party, have done things differently, thereby altering the negative
course the revolution was taking? Did the left, including the Tudeh
Party, make any mistakes, in your estimation?

The Iranian Revolution successfully completed its political phase of
overthrowing the Shah’s despotic regime. It was clear to our party that
for the revolution to succeed, it needed to evolve into its social
phase, replacing the socio-economic order it had inherited from the
Shah’s regime with a new order.
Many of our party’s slogans and our platform—including the
nationalization of banks and multinational companies, as well as land
reform—was carried out in the atmosphere that existed in the first year
of the revolution. However, constant U.S. and reactionary interference
in Iran, including the imposition of the imperialist-instigated
Iraq-Iran War, stopped the revolution in its tracks and provided the
backdrop for Khomeini and his followers to stop these programs and move
towards the establishment of a theocratic regime.
At the time, conscious of challenges facing the revolution, our party
called for the formation of a “people’s united front” with other
revolutionary forces to make sure that the revolutionary movement would
not be derailed, but this did not materialize due to significant
political differences among those forces.
Our party, in its analysis of the early years of revolution,
concluded that in our policy of “critical unity” with Khomeini and his
followers, we were perhaps more concerned with unity than being critical
of some of the policies that clearly were not in line with
revolutionary ideals and the people’s demands. It is clear that had the
left-democratic forces managed to come together, it would have been
possible to change the balance of forces politically in the country for a
different outcome. The reactionary forces, in a matter of three years,
were able to attack the left and democratic forces one-by-one and then
establish their absolute rule in Iran.
The major slogans of the 1979 Revolution were for
freedom, independence, and the establishment of a republic, with
democratic rights and structures, to replace the Shah’s dictatorship.
What is the Tudeh Party’s assessment of the outcome of the revolution
for democracy, gender equality, the rights of ethnic and religious
minorities, and trade union rights in Iran?
Iran, 40 years after the revolution, is ruled by a despotic regime
with no regard for human and democratic rights. Over past decades, we
have witnessed laws restricting women’s rights and their treatment as
second-class citizens. This has included medieval laws permitting the
marriage of girls as young as 11, as well as enforcing gender
segregation in places of education and even hospitals.
The regime has also ruthlessly suppressed the basic rights of ethnic
and national minorities, as well as religious minorities. Its record on
trade union rights remains appalling. Many trade unionists are
imprisoned or exiled and trade union activity either restricted by the
state or forced underground. The regime has never accepted the legal
operation of trade unions. It only permits Islamic Labor
Councils—tripartite bodies involving the employers, government
representatives, and employees—thus breaching ILO Conventions 87 and 98,
guaranteeing all workers the right to belong to a trade union of their
choice and engage in trade union activities.
During the past forty years, many significant social
movements have demanded, and continue to demand, change in Iran. Have
these movements aimed to reform the political and socio-economic system
in Iran, or have they been directed towards a more fundamental change in
the social order?

Over the past two decades, powerful social movements have emerged in
Iran demanding change in the way the country is ruled and rebelling
against corruption and repression. In 1997, Mohammad Khatami became
Iran’s president promising reform and the “rule of law.” There was a
powerful social force, from women to youth and students, behind Khatami,
and he received over 20 million votes in the election.
But his government’s promises were not realized due to their
overriding belief that change could only take place if permitted by the
“Supreme Religious Leader” and could not cross the “red lines” of the
Islamic Republic. Over the eight years of Khatami’s presidency, despite
some respite in terms of the oppression, real changes to Iran’s power
structure never materialized, and the regime was able to neutralize the
social movements and gain the initiative against them.
Socio-economic conditions continue to worsen in Iran. Poverty is at
unprecedented levels, with some estimating 40 percent of the population
being below the poverty line, all while the regime has sold over $800
billion worth of oil over the last three decades. Now we are witnessing a
radicalization of people’s demands amidst growing workers’ strikes and
protests. In late 2017 and into 2018, we had sporadic protests in 80
Iranian cities which the regime suppressed savagely. And over the past
three months, we have been witnessing prolonged workers’ strikes in key
industries such as steel, automobile, and sugarcane in the south of
Iran. People are demanding an end to the current neoliberal policies of
privatization, economic hardship, and the unprecedented levels of
corruption.
One of the characteristics of the 1979 Revolution was its
then-stated “anti-imperialist” position. Some of the acts of the
theocratic leadership were seen by some on the left as having a
progressive motivation, as Iran’s way of protecting its sovereignty. How
does the Tudeh Party assess the theocratic leadership’s stated policy
of being opposed to U.S. imperialism? Is it sincere? Has the foreign
policy of the Islamic Republic of Iran benefitted the Iranian people in
any way?
It is true that one of the key characteristics of our revolution was
its anti-imperialism, and especially in opposition to U.S. imperialism,
due to their long-term interference in our country and plundering of our
national resources, including oil and gas. The religious leaders used
these slogans, which were mainly viewed as Tudeh Party slogans, to
consolidate their position in the revolutionary movement
Clearly, their anti-American slogans were not based on the same
understanding as the anti-imperialist slogans of the left and our party,
which reflected our view of the destructive role of monopoly capital on
the world stage and our belief that anti-imperialist forces should
unite and work together to build a different world. The Iranian regime’s
ideal economic model was that of a capitalist order wrapped up with
empty Islamist slogans.
For the Iranian regime, its influence in the region and the building
of an Islamic empire was a critical part of its foreign policy and, as
such, clashed with that of reactionary and puppet regimes in Saudi
Arabia and other Arab states in the Persian Gulf region. It is also
important to note that at the most critical points in our region’s
recent history, including the imperialist aggression in Afghanistan and
Iraq, the Iranian regime—according to its own leaders—helped U.S. plans
by opening up the country’s airspace so that attacks could be carried
out against both neighboring countries.
The Trump administration is now openly following a policy
of regime change in Iran. What is your party’s position on the
possibility of such an external intervention? Can you give us your
opinion about the activities of President Trump, the Israeli government,
Saudi Arabia, and their allies?
In a statement by our Central Committee on May 1, 2018, in response
to the growing threat from the U.S. and its allies, our party opined
that: “In analyzing the current developments in the Trump administration
and the coordination—more than ever before—of the governments of Israel
and Saudi Arabia with that administration, many of the world news
agencies have commented that the risk of a military conflict between
Israel and Iran is now higher than ever.”
We further elaborated that: “Our country and the Persian Gulf region
and the Middle East is once again faced with a very serious and urgent
threat of catastrophic military conflicts which will have dire
consequences for Iran and the entire region. Ignoring these threats and
supporting the destructive and interfering policies of the U.S., Israel,
and Saudi Arabia, contrary to the claims of some of the foreign-allied,
anti-people, so-called opposition not only will not lead to the
liberation of Iran from the claws of the current theocratic regime but,
like the imperialist-inflicted war of Iraq with Iran (1980-88), will
have very damaging consequences for our nation, and for the popular
movement for freedom, sovereignty, and social justice. The struggle of
the Iranian people to dispose of the theocratic rule and establish a
national and democratic regime in Iran…is not achievable through the
destructive military intervention of such reactionary forces as the
Trump, Netanyahu, and Bin Salman administrations. In such critical
times, the most important task of all the national and democratic forces
is to organize and mobilize all peace-seeking forces of the nation and
the world to prevent another disastrous and destructive war in our
region.”
What is the attitude of the Tudeh Party and the
progressive and labor movement toward the sanctions imposed by the Trump
administration against Iran? How do the sanctions hurt progressive
forces?
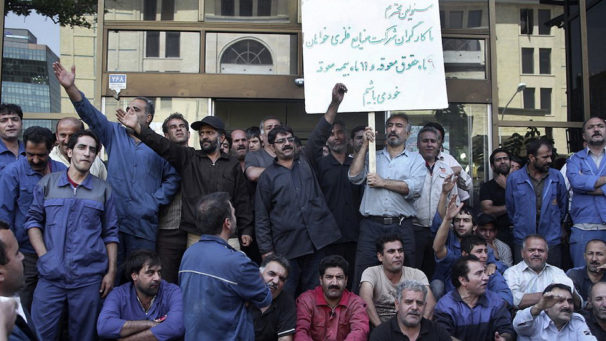
The Trump decision, in complete contravention of world public
opinion, to take the U.S. out of the 2015 Joint Comprehensive Plan of
Action (JCPOA) Agreement with Iran…has significantly increased tension
in the region and raised the threat of a new devastating war in the
Middle East.
We condemn the re-imposition of economic and banking/monetary
sanctions on Iran, which constitute an illegal violation of an
international agreement ratified by the UN Security Council and mostly
hurt the ordinary people of Iran. It is worth mentioning that similar
sanctions against Iraq, prior to the U.S.’ military attack on that
country in 2003, cost the lives of hundreds of thousands of vulnerable
citizens, including children and the elderly.
Despite Trump’s claim that his actions will help the Iranian people’s
struggle, it is clear that U.S. policy is to change the course of the
Iranian people’s struggle and facilitate a regime change to establish a
puppet government.
The struggle of the Iranian people against the religious dictatorship
in Iran can only be determined by the Iranian people and its
progressive forces. The backing of John Bolton and the Trump
administration for the Pahlavi family (the family of the deposed Shah of
Iran) and the so-called “National Council of Resistance” headed by
Maryam Rajavi—who for many years received the patronage and protection
of Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein and who currently receives hundreds of
millions of dollars’ worth of support from the criminal Bin Salman
government regime in Saudi Arabia—clearly shows the real intentions of
the U.S. government towards Iran and our peoples’ struggle.
The Tudeh Party of Iran, along with other progressive forces in our
country, view U.S. sanctions and its interference in Iran as directly
opposed to the national interest of our country and our peoples’
struggle against the dictatorship in Iran.
What objectives is the Tudeh Party pursuing at this stage of the struggle for the transformation of your country?
Forty years after the victory of the 1979 Revolution, Iran is in need
of fundamental and democratic change. The future of our country should
be determined by our people, without external interference, through the
establishment of a democratic political system.
Iran has remained at the stage of National Democratic Revolution and
the Tudeh Party of Iran is committed to our country realizing the
following objectives: safeguarding national sovereignty; rolling back
and eliminating the neoliberal economic restructuring implemented by the
Islamic Republic; limiting and directing the growth of capitalism
towards the growth and development of the productive forces of our
national economy; the fair redistribution of materials and wealth; and,
the realization of democratic freedoms and social justice.
The Tudeh Party of Iran continues to believe that such a change
requires the formation of a united anti-dictatorship front by
mobilizing all social forces within our country and the emergence of a
strong union of left and progressive forces with effective participation
of the working class.
The Tudeh Party of Iran believes the most urgent goal of the
progressive forces in Iran is that they work together to prepare the
grounds for ending the absolute rule of the Supreme Religious Leader
once and for all, in order to open the way for fundamental democratic
and enduring change in our country.
Τετάρτη 1 Μαΐου 2019
1η Μάη 2019
1η Μάη 2019.
Η ιρανική εργατική τάξη βρίσκεται εδώ και δεκαετίες εγκλωβισμένη σε ένα αδιέξοδο δίλημμα:
Να διεκδικήσει ανυποχώρητα τα δικαιώματά της χωρίς να φοβάται το ενδεχόμενο μια εξέγερση της ενάντια στο θεοκρατικό καπιταλιστικό καθεστώς να χρησιμοποιηθεί-εργαλειοποιηθεί από τις δυτικές ιμπεριαλιστικές δυνάμεις και το αμιγώς πλέον ακροδεξιό Ισραήλ για να διαλύσουν και αποικιοποιήσουν δια της ψευτο-ομοσπονδιοποίησης την χώρα που ζει; με εκατοντάδες χιλιάδες θύματα και το έθνος κατεστραμμένο;
Ή να συνεχίσει να κάνει υπομονή και να δέχεται την ηγεμονία των θεοκρατών για να μην καταστραφεί η χώρα από τους λύκους που την περιτριγυρίζουν διψασμένοι για θάνατο και καταστροφή, με αποτέλεσμα όμως αυτής τής υπομονής την συνέχιση τής καταστολής της, και την ενδυνάμωση των αντιδραστικών αντιιμπεριαλιστών δολοφόνων;
Αυτό το δίλημμα είναι δικό της αλλά αν θεωρήσουμε ότι η εργατική τάξη του Ιράν, οι εργαζόμενοι της χώρας αυτής και τα φτωχά λαϊκά κοινωνικά στρώματα, είναι μέρος τής παγκόσμιας εργατικής τάξης, μέρος του παγκόσμιου λαού, τότε το δίλημμα είναι και δικό μας.
Πως θα απαντούσε ένα αυτόνομο δημοκρατικό ταξικό κίνημα σε μια άλλη χώρα στην αγωνία αυτών των ανθρώπων;
Πως θα απαντούσαν άραγε οι ξερόλες διανοούμενοι στην δύση και οι πολυάριθμες σεκταριστικές και ρεφορμιστικές αριστερές, κομμουνιστικές, αναρχικές ομάδες και οργανώσεις στην δύση και την Ελλάδα; πως θα απαντούσε άραγε το πρώην-κομμουνιστικό ΥπερΚόμμα ελλάδας; η Λαέ, οι Εξαρχειώτες;
Είμαι σίγουρος ότι όλοι αυτοί έχουν την απάντηση έτοιμη:
Η μια αντίθετη και συμπληρωματική προς την άλλη.
Η μια αντίθετη και συμπληρωματική προς την άλλη.
Τα συγχαρητήρια μου σε όλους.
Στις πορείες σας τώρα, άντε και καμιά μολότωφ να περνάει η ώρα..
Ζήτω η ιρανική εργατική τάξη και ο ηρωικός πολιτισμένος λαός τού Ιράν!
Ζήτω η ιρανική εργατική τάξη και ο ηρωικός πολιτισμένος λαός τού Ιράν!
Ιωάννης Τζανάκος
Πουθενά-Πουθενάς
Σάββατο 13 Απριλίου 2019
Δεν έχει αλλάξει τίποτα..
Αναδημοσίευσα έναν λόγο τού Ν.Μπουχάριν και ένα άρθρο του Κ.Κάουτσκι, σε αντίστιξη, και χωρίς να έχω την πρόθεση να προβώ σε "εμβριθείς" αναλύσεις, για να σας "δείξω" πως οι αντινομίες, οι αντιφάσεις και τα αδιέξοδα τού περιλάλητου "κινήματος", ήδη στις "δοξασμένες" εποχές του, χτυπάνε κόκκινο, είναι τυφλές, και σημαίνουν ένα στρατηγικό ανθρωπολογικό πρόβλημα που δεν πρόκειται να "αρθεί" εύκολα με την ανάκληση αγνών "θεμελίων" ή την επίκληση τής "νέας" εποχής τού καπιταλισμού ("ολοκληρωτικός καπιταλισμός" και άλλες ανοησίες).
Ο Κάουτσκι εκφράζει, ως ένα (συκοφαντημένο από τους αντι-σοσιαλδημοκράτες) ακέραιο πρόσωπο, την κοινοτοπία αλλά και την βαθιά δύναμη τού δημοκρατικού σοσιαλισμού, με όλες του τις ρεφορμιστικές αντιφάσεις και τους περιορισμούς αλλά και την δέσμευσή του στις αξίες της ελευθερίας τής δημοκρατίας και του αλληλοσεβασμού.
Η έλλογη κρίση του για τις απολυταρχικές μεθόδους των μπολσεβίκων είναι προφητική και εύστοχη, αν και δημιουργείται ως κρίση από την θέση υπεράσπισης ενός συμβιβαστικού μεταρρυθμιστικού σοσιαλισμού.
Η έλλογη κρίση του για τις απολυταρχικές μεθόδους των μπολσεβίκων είναι προφητική και εύστοχη, αν και δημιουργείται ως κρίση από την θέση υπεράσπισης ενός συμβιβαστικού μεταρρυθμιστικού σοσιαλισμού.
Η θέση του Μπουχάριν απέναντι στον "αριστερισμό" (Γκόρτερ και άλλοι υπερκομμουνιστές τής εποχής) και τον αναρχοσυνδικαλισμό, είναι αποκαλυπτική για τις μπλανκιστικές και αυταρχικές θέσεις των μπολσεβίκων, αλλά εμπερικλείει ως θέση μια σημαντική δύναμη κυνικής-ρεαλιστικής αλήθειας.
Βέβαια ο ίδιος ο Μπουχάριν δεν είχε την εποχή που έκανε τον διδάσκαλο στους αριστεριστές για τον "αντιαυταρχισμό" τους επίγνωση τής μελλοντικής δικής του μοίρας, όπως αυτή προκλήθηκε από την δράση του "επαναστατικού" μηχανισμού που υπερασπίστηκε και συνοργάνωσε μαζί με άλλους ομοϊδεάτες του.
Στο βάθος όλων αυτών, δια μέσω των επιχειρημάτων του Μπουχάριν, ακούμε την ίδια υστερική αριστερίστικη φωνή που τα καταγγέλλει όλα αυτά (και τον Μπουχάριν), και αυτή προφητικά αλλά όχι με τον ίδιο τόνο και προσανατολισμό όπως η προφητεία τού Κάουτσκι, αλλά χωρίς επίσης να προτάσσει ούτε ένα λογικό επιχείρημα.
Βέβαια ο ίδιος ο Μπουχάριν δεν είχε την εποχή που έκανε τον διδάσκαλο στους αριστεριστές για τον "αντιαυταρχισμό" τους επίγνωση τής μελλοντικής δικής του μοίρας, όπως αυτή προκλήθηκε από την δράση του "επαναστατικού" μηχανισμού που υπερασπίστηκε και συνοργάνωσε μαζί με άλλους ομοϊδεάτες του.
Στο βάθος όλων αυτών, δια μέσω των επιχειρημάτων του Μπουχάριν, ακούμε την ίδια υστερική αριστερίστικη φωνή που τα καταγγέλλει όλα αυτά (και τον Μπουχάριν), και αυτή προφητικά αλλά όχι με τον ίδιο τόνο και προσανατολισμό όπως η προφητεία τού Κάουτσκι, αλλά χωρίς επίσης να προτάσσει ούτε ένα λογικό επιχείρημα.
Τίποτα δεν έχει αλλάξει, και δεν διαφαίνεται κάτι που να μπορούσε να τα κάνει "όλα αυτά" στιγμές που ξεπερνιούνται σε μια ευρύτερη διαλεκτική μετασχηματιστική-επαναστατική διεργασία.
Ιωάννης Τζανάκος
Nikolai Bukharin / Third Congress of the Communist International - Speech in Discussion of Tactics and Strategy - July 1, 1921
Speech in Discussion of Tactics and Strategy - Marxists Internet Archive
Source: Published in To the Masses: Proceedings of the Third Congress of the Communist International, 1921 (https://www.haymarketbooks.org/books/897-to-the-masses), pp. 508-515
Translation: Translation team organized by John Riddell
HTML Markup: David Walters for the Marxists Internet Archive, 2018
Copyright: John Riddell, 2017. Republished here with permission
Translation: Translation team organized by John Riddell
HTML Markup: David Walters for the Marxists Internet Archive, 2018
Copyright: John Riddell, 2017. Republished here with permission
Comrades, the comrade who spoke before me, Comrade
Malzahn, objected to the tone adopted by Comrade Heckert. However,
Malzahn himself spoke in a similar tone. As a result, I am obliged to be
as meek as a little lamb. (Laughter) In the present discussion
of different positions and problems, in my opinion, we have quite often
spoken of things that are truly obvious. So, for example, when Comrade
Hempel of the KAPD spoke here of new methods of mass action, that is a
quite obvious matter for us here. We discussed this theme in some detail
even before the War. It is just as obvious that, as regards what has
been said here about offensives in general, even Comrade Lenin
recognises that there is no Marxist who could speak against offensives
in general. It would therefore be perhaps desirable, to include that
sentence by Comrade Lenin in the theses. (Laughter)
Trotsky: But only using the wording of Comrade Lenin: ‘Only asses could believe the contrary.’
Bukharin: In discussing the world situation as a
whole, we must keep in mind that it is not at all excluded for the
relative temporary equilibrium that seems to prevail in Europe to be
suddenly disrupted, and for the situation in this or that country to
suddenly change. In this regard, Comrade Lenin spoke of a number of
things, and his remarks need to be interpreted somewhat – of course, to
be interpreted strictly in the fashion of Lenin. Let me provide some
examples.
In the first phase of our revolution, the Central Committee of our
party sent instructions to all our agitators to protest against the
shameless lies of the bourgeoisie, who claimed that we, the Bolsheviks,
were for civil war. Those were our own instructions. And in the
situation at that time, these instructions were entirely correct. Now if
we take quite a different situation, for example, just before the
October Revolution, this sentence and these instructions would be not
only completely wrong but completely criminal. At that time, of course,
we gave all our agitators instructions to carry out an uprising and
engage directly in civil war.
Let us take a second example, which comes from after the winning of
political power. During the [1918] Brest-Litovsk Peace, our party and
Comrade Lenin, the recognised leader of our party, were for the
Brest-Litovsk Peace, as you all know. Later, during the [1920] Polish
events, the same Comrade Lenin was for the offensive, for a military
policy. That was absolutely correct, of course. These examples show that
the tactical line is something that is not fixed but is absolutely
in motion, always determined by the specific position, specific
conditions, and the specific conditions. If we can grasp that, we will be able to deliver a warning to comrades who find Comrade Lenin’s speech to be undialectical. (Laughter)
We all know very well that the future Executive, however it is
composed, must heavily upbraid any party that, under certain
circumstances, does not take the offensive. In other words, the general
tactical line proposed in the theses by the Russian delegation cannot
be used as justification for all conceivable future vacillations
committed by opportunist forces inside the Communist Party. (Loud applause)
Now a few words about conditions in Germany. A certain entirely
undialectical contradiction exists among the different comrades. On the
one hand, it is said that we must study our errors very carefully, and,
on the other, that we should talk only of the future. In my opinion that
is not a contradiction but an absurdity. We must, should, and will talk
about the conditions. Despite the various remarks of Comrade Malzahn, I
will say a few words about the Levi affair, because it is by no means a
personal matter but concerns a current. And we know very well that
there is sill a certain political affinity between certain forces in the
German party and Paul Levi. To continue to speak about the March Action
now and going forward would be quite strange, since a great deal has
been said already. Nonetheless, I would like to analyse certain passages
of Levi’s most recent article, passages showing us that Levi has now
developed into a quintessential Menshevik.
I will start with the question, ‘sect or party,’ which as you know
plays a major role. When we look back on the past and recall what Levi
did during the Second Congress, it is clear that during the congress he
said that the Communist International should be pure, that it would be a
crime against the Communist International to admit syndicalist trade
unionists. If we do that – these were his very words – that action will
amount to burying the International. (Shouts: ‘Hear, hear!’)
That is what Paul Levi said during a session of the Executive. Now he
has turned around completely. Now Levi is claiming that we were against
mass parties and mass organisations of the proletariat. That is no
dialectical contradiction. Rather it means that Levi is seizing hold of
any argument in order to break free of the party. In the question of the
relationship of masses to leadership, Paul Levi spoke out quite sharply
against the KAPD, and rightly so, referring to this group’s lack of
understanding of the role of leadership in a mass party. Now, however,
an article by Levi expresses solidarity with a group within the Russian
party, namely the so-called Workers Opposition, which is the embryo of
the tendency that is fully developed in the KAPD.1
This appears in black and white in Levi’s last article. That tells us,
once more, that Levi grasps at any tool to destroy the big workers’
party, the Communist Party. (Loud applause)
Let us take a third question, ‘the struggle for the dictatorship of
the proletariat’. For us, this struggle is of course self-evident. Even
Levi could not think otherwise. Taking his most recent article, we find
the following on conditions in Russia:
It seems to us that creating the possibility of
political struggle is all the more urgent, given that Russia has entered
the phase of granting concessions.2
What is that supposed to mean? The text of the article as a whole
indicates what it means. Levi says that the situation in Russia is not
yet sufficiently clear. In his view, Russia today is undergoing a
political and social crisis. The Communist Party needs to make a
correction in order to find the right path. From what side will this
correction come? From the side of the Social Revolutionaries, of course,
from the side of the Mensheviks, that is, against the dictatorship.
That is clearly specified here. Of course this signifies a blow against
all the policies of the Russian party. This also has a certain
relationship with what Levi said earlier against Moscow and Moscow’s
dictates. Aside from that, these are psychological considerations. From a
logical point of view, what we have here is the embryo of a conception
that is directed against the dictatorship of the proletariat as such. (Loud applause) Of course, this is a fully Menshevik conception. To express it differently, this is the transition from the concept of the dictatorship to that of free democracy. There is no other way to interpret it.
Then we have, in addition, the question of the dictatorship of the
party. We Marxists – at least, we orthodox Communists – have always
maintained that the dictatorship of a class can be expressed only
through the dictatorship of the vanguard of that class; that is, the
dictatorship of the class can be realised only through the dictatorship
of the Communist Party. We have always rejected the entirely absurd
concept that counterposes the dictatorship of the class to the
dictatorship of the party. That is nonsense. And Levi was with us
completely on that point. Now we find, in his most recent pamphlet,
ideas regarding Russian affairs, but there are also conceptions that
attempt to generalise the Russian experience. We read there:
Every dictatorship of the proletariat is a dictatorship
of Communists, but not every dictatorship of Communists is a
dictatorship of the proletariat.
So if there is a rift between the proletariat and the Communist
Party, then the dictatorship of the Communist Party is not the
dictatorship of the proletariat. In response, I would ask: how do we
determine in this case the classes in the party? Is it possible, from a
Marxist standpoint, to form a classless party? Yes or no? Obviously, as
Marxists, our answer to this question must be ‘no’. There is no
classless party. It follows that if the Communist Party is at the helm,
it represents the interest of some class. What class? If it is a
Communist Party, it represents the interests of the proletariat.
So what can be the meaning of this sentence of Levi’s? The sentence
has and can have only one meaning, namely, a concept hostile to the
party dictatorship. From a purely theoretical point of view, the
following situation may arise: The proletariat becomes demoralised. The
party governs. The party does not have the support of the entire
proletariat, and perhaps not even the majority of the proletariat. Now
tell me please, in such a situation, where a part of the proletariat has
been declassed, does the ruling party not represent the interests of
the proletariat? In such a case, who does represent the real interests
of the proletariat? The party, of course, the ruling party. What then is
the point of all this talk? The goal of this chatter is simply to
develop the embryo of a line of thinking opposed to the dictatorship of
the proletariat as such and therefore for bourgeois freedom, for democracy. This line of thought is absolutely clear.
We can observe that the embryo of such liberal concepts is also found
in the KAPD. I have touched on this question deliberately because I
consider this ideology and these symptoms very dangerous. In my opinion,
this signifies the road to the Mensheviks and the road out of the Communist Party. (Loud applause)
We must therefore draw the following conclusions: An energetic battle
must be waged against such tendencies, or the remnants of such
tendencies, in all parties, including the German party. Every formation,
every group that crystallises out of such conceptions must be
immediately dissolved. In my view, we must put an end to the opposition
faction, as such, within the German party. (Loud applause)
I will now move on to another question, that of the KAPD. Comrade
Hempel declares that we do not need leaders or theoreticians. This
statement, in my opinion, stands as evidence that hatred of leaders is
so strong in this party that it has made a poor choice of leaders. (Laughter)
This party publishes various educational pamphlets and propaganda
articles. Among the pamphlets we find one by their main theoretician,
Hermann Gorter, Class Struggle and the Organisation of the Proletariat.
This pamphlet presents the KAPD’s line of thinking and ideology much
better than the speech of Comrade Hempel today. Gorter is not such an
adroit diplomat as Hempel, although Gorter is a man of letters and
Hempel an ordinary worker. By the way, we heard another ordinary worker
today, Comrade Burian. Now let us listen to what Gorter says in this
pamphlet.
The greatest weakness of the German and world revolution and one of
the main causes of its defeats is the fact that it is not guided by a
policy that is scientific, that is, historic-internationalist.
As we shall see, Gorter writes like a good Christian cleric. He continues:
In determining tactics and strategy, the question of productive and
class relations in Germany, Western Europe, and America was not given
priority and perhaps was not considered at all. The main responsibility
here lies with the Russians – Lenin, Zinoviev, Radek, etc. – and the
entire Third International.
The idea expressed in this sentence is then developed in the pamphlet
along various lines. That was from page 1. At the end of the pamphlet,
Gorter writes as follows:
The Kronstadt proletariat revolted against you, against the Communist
Party. You proclaimed a state of siege in Petersburg that was also
aimed against the proletariat. (Given all your policies, you had no
choice in the matter.) After doing that, did it not occur to you that it
might be better to have a dictatorship of the class rather than one of
the party? And that it would perhaps be better in Western Europe and
North America to have a dictatorship not of the party but of the class?
And that the ‘Lefts’ are perhaps right after all?
To wrap up, he writes:
If the Russian policies of party and leader dictatorship are still
pursued here, after the disastrous results they have already produced,
that is no longer a matter of stupidity but a crime. A crime against the
revolution.
So first Gorter says that for agrarian Russia the only correct policy
is a dictatorship of the party. Naturally that does not apply to the
developed capitalist countries of the West. Consequently, it is a crime
against the International and the revolution to mix up these two
different things. Then, on the last page, he says that mistakes have
been made in Russia, and that KAPD policies must be applied in Russia as
well. (Protests from the KAPD representatives) Dear comrades
of the KAPD: it’s written here in black and white. Let me cite a Russian
proverb. It says, ‘The crocodile is as long from tail to nose as it is
from nose to tail.’ (Laughter) That goes for politics as well.
The final page of Gorter’s pamphlet refutes completely what he said
on page 1. So there is no difference between Russia and North America,
and vice versa. Then Gorter tells us about the trade unions, and that to
impose the relationships of agrarian Russia on distant countries is a
bankrupt policy. The trade unions are outmoded institutions and are
therefore of no use.
KAPD representatives: That is not true.
Bukharin: Dear comrades, that is written here in
black and white. Tell me, why should we not apply exactly the same
policy to the parties? The parties, too, arose previously; they too
arose in an earlier period. You respond that this is why the Social
Democracy is of no use. That means, it follows, viewing the question by
analogy, that the old trade unions were also useless. What has happened
to the parties must also have happened to the trade unions. Either the
one or the other. And if you apply the line of reasoning you have
developed for the parties to the trade unions as well, the picture
becomes quite clear. The old trade unions really had quite different
functions, which by no means justifies the entire theory of the trade
unions presented by Comrade Hempel in his speech today. We carried out a
theoretical and practical struggle with the trade unions in Russia and
in other countries. We always fought against those views on the
trade-union question. We said that the unions are mass organisations of
the proletariat, which must be educated toward the final struggle
together with the party, together with the other party organisations.
You have not offered any counter-argument.
Gorter relies here on quite a curious argument. Completely distorting the matter, he declares:
Our modern Western European and American world is
cartelised, imperialist, and based on banking capital. In such a world,
capital is no longer organised by trades but rather by enterprises.
So, not by trades but by enterprises. That is completely wrong. It is
not a matter of enterprises, or even branches of production, but by
various combinations of production branches. What Gorter says is
complete nonsense. Suppose it were true, what would that tell us,
according to Gorter? It would mean that we should also consolidate our
trade unions. Gorter provides no other evidence, and neither does
Comrade Hempel. You cannot say that new epochs demand new organisations.
New organisations are all very good, but experience teaches us that the
old organisations should not be given up. The sentence about organising
by enterprise is wrong, factually speaking. All you can conclude from
that is simply that the trade unions should be organised in the same
fashion as production is. If you are satisfied with such generalities,
why not apply this to the party as well?
The arguments about the relationships among the parties and between
the leadership and the masses are just as weak. Gorter says that the
party was able to win in Russia because the proletariat was small. In
other countries, capitalism is enormously large and the enemy is much
bigger and stronger, and therefore we do not need any leadership or
party in the strict sense of the word, but rather entirely different
organisations. I must reply that the entire argumentation is completely
wrong. The party and the leaders cannot be counterposed one to the
other. If we have a large party, it must have a central committee. What
does ‘central committee’ mean? It means simply the leadership.
The [chair’s] bell has given me a signal. So in conclusion I will say
only this to the comrades of the KAPD: You maintain that you are good
Communists, as stated by your theoretician, who considers himself a
representative of a proletarian party that is better than us. Any
halfway intelligent person tries to establish the social causes of the
crisis [in Russia]. How did this crisis find expression? Simply through
an attempt at a peasant vendee aiming to overthrow the proletariat.3 You do not want to recognise that, and still you say, ‘We are a more proletarian party than you.’
KAPD representatives (raising objections): That’s a slander!
Bukharin: That is no slander. It’s written here in black and white. What other sense could these words have?
Radek: No sense at all. It’s nonsense. (Laughter)
Bukharin: In my view, we must tell the comrades that
these goals and these ideas unite the KAPD fully with its most hated
enemy, with Paul Levi. You stand on the same theoretical foundation as
Paul Levi.
KAPD representative: And what about in practice?
Bukharin: Given that your practice is rather
different from your theory, that shows you to be complete muddle-heads.
That is why we call on the KAPD comrades not to let themselves be led
astray in this fashion by their leaders. Their leaders must not write
such things, otherwise we will have to finish off with the entire party.
(Loud applause)
Notes
1.
The Workers Opposition was a group within the Russian CP that led by
Alexandra Kollontai, Aleksandr Shlyapnikov, S.P. Medvedev, and others.
Formed in September 1920, it called for trade-union control of
industrial production and greater autonomy for CP fractions in the
unions. After its position was rejected by the Tenth CP Congress in
March 1921, the Workers Opposition subsequently raised criticisms of
measures adopted introducing the NEP. Following its censure at the
party’s Eleventh Congress in March–April 1922, the Workers Opposition
ceased organised activity.
2. Levi, ‘Von den Konzessionen’, published in Unser Weg
(Sowjet), 6 (15 July 1921), pp. 167–72. ‘Concessions’ here refers to
Soviet Russia’s willingness, under the New Economic Policy, to permit
limited foreign investment projects, subject to government control.
3.
Vendée is a department in northern France that was a centre of royalist
and peasant insurrection against the French Revolution from 1793 to
1795.
Karl Kautsky / The Moscow Trial and the Bolsheviki. Preface to The Twelve Who are to Die: The Trial of the Social Revolutionists in Moscow (1923)
The Russian Party of Socialists-Revolutionists differs
radically from the Social-Democratic Party; nay, more, both parties
disagree in their basic conceptions of policy and principle.
Nevertheless, I gladly accepted the invitation to write a preface to the
book on the Moscow trial, published by the Party of
Socialists-Revolutionists. More than that: I feel that I not only have a
right but am duty-bound to write this preface, in the name of my
social-democratic principles. For these principles indicate clearly that
the proletariat, as the most exploited and enslaved of all classes,
cannot emancipate itself without emancipating at the same time all those
who are enslaved. A proletarian, Socialist party cannot fulfill its
great, historic mission without making itself the protector of all the
enslaved and oppressed.
For this reason, Marx and Engels took up the cudgels in behalf of
oppressed Poland and raised their voices in defense of Ireland. For this
reason, Socialists always fought for the liberation of native peoples
suffering under the colonial domination of imperialist governments. And
in doing so, Socialists frequently cooperated with non-socialist,
bourgeois elements. We are, therefore, all the more obliged to come to
the defense of the persecuted and oppressed when they belong to a party
which, like ours, although not always in the same way, seeks the
emancipation of the toilers, a party which, like ours, had for many
years waged bitter, holy war against the meanest enemy of the world
proletariat, – Russian absolutism. The fight waged today by the
Socialists-Revolutionists is but a continuation of the old fight. For
there is no substantial difference between an absolutist government
which holds its power by heritage or one which is of recent creation.
There is no material difference between the rule of a “legal” Czar and a
clique that accidentally established itself in power. There is no
difference between a tyrant who lives in a palace and a despot who
misused the revolution of workers and peasants to ascend into the
Kremlin.
And the fact that the new Russian despotism is bonapartist rather
than czarist in character makes it all the more essential for the
Socialist parties of the world to come to the defense of the Russian
Socialists persecuted by this bonapartist regime. For what this regime
seeks is to make the Socialists of the entire world its associates in
its policy of persecution, – something which Czarism, for obvious
reasons, never aimed at. The Bolshevist rulers want the Socialists of
the whole world to applaud their persecution of the
Socialists-Revolutionists and Mensheviki, but the time has passed when
they could expect their assertions to pass unchallenged.
The Bolsheviki maintain that their policy constitutes the only
genuine application of Marxism, that it constitutes a strict application
of the principles of the class struggle. But the oppression and
persecution of workingmen, belonging to another current of Socialist
thought, and for no other reason than that these workers prefer to
interpret Socialism in a manner different from the Bolsheviki, is in
sharp contradiction with these class-struggle principles. We, Marxian
Social-Democrats, in common with nearly all other Socialists, stand for
democracy and for the right of unrestricted political propaganda for all
political parties. This right of unrestricted propaganda we must, above
all, demand for all the Socialist parties in Russia. It is quite
inevitable for the respective Socialist parties to find themselves
frequently in disagreement with one another. But this must be expressed
only in a struggle of argument, in a struggle for the soul of the
proletariat. Socialists who resort in this struggle against the opinions
of other Socialists to guns, bayonets, Che-Ka organizations and jails
are committing an act of violence against the proletariat and the idea
of the class struggle.
Even the Bolsheviki themselves feel this. For this reason they seek
to excuse their regime of violence in the eyes of the Socialists of the
entire world by asserting, like the wolf in the old fable, that the
sheep are trying to pollute the water which they, the Bolsheviki,
forsooth seek to maintain unpolluted. To convince the world of the truth
of this claim was the chief purpose of the Moscow trial. By this trial
the Bolsheviki sought to destroy not only physically but morally the
foremost representatives of the Socialists-Revolutionists. But the trial
produced quite the opposite effect. It resulted in the moral victory of
the accused and the moral execution of the accusers.
The Bolsheviki were first to use violence against other Socialists.
They dissolved the Constituent Assembly not by way of resistance against
any violence on the part of the Socialists-Revolutionists and
Mensheviki but because of their realization of their own inability to
obtain the support of the majority of the peasants and workers by means
of free propaganda. This was the fundamental cause of the Bolshevist
coup d’etat against the representatives of the revolutionary workers and
peasants. Hence, the abolition of all rights of all other Socialists
who refused to submit to the crack of the Bolshevist whip. Hence, the
establishment of a political regime which leaves but one form of open,
political action for the opposition – civil war. The Social-Democracy
was never averse to the use of violence in resistance against violent
persecution. It simply made the advisability of the use of such violence
conditional upon considerations of purpose and the possibility of
success. If the Social-Democracy found itself in disagreement with the
Socialists-Revolutionists in this regard, it was not from considerations
of principle but of tactics. But, if I am correctly informed on this
point, there are no substantial differences of opinion at the present
moment between the Socialists-Revolutionists and the Mensheviki. Both
recognize that an anti-Bolshevist uprising at the present moment could
not be successful and would even, under certain circumstances, lead to a
result diametrically opposed to that sought, by provoking foreign and
reactionary intervention. Armed uprising against the Bolsheviki, at the
present moment, would only delay the process now in progress in Russia
and pregnant with great consequences, – the process of the desertion of
Bolshevism by the proletarian and peasant masses and their return to the
other Socialist parties. This process represents a deadly danger for
the Bolshevist dictatorship. The real crime of which the
Socialists-Revolutionists are guilty before the Bolsheviki at the
present moment is not in the preparation of terroristic acts and armed
uprisings, but in that, like the Mensheviki and perhaps even to a larger
extent, the Socialists-Revolutionists, whose ranks are constantly
growing in number, are acquiring in ever increasing measure the
confidence of the toiling masses of Russia. This bids fair to bring
about the complete isolation of the Bolsheviki in a short time, so that
the only ones who will stand behind them will be a few capitalists and
the Red Army. Nor is the army, too, likely to continue its support of
the Bolsheviki very long, for military dictatorships must have military
successes abroad and cannot thrive merely upon suppression of uprisings
of hunger-driven peasants. In vain do the Bolsheviki seek to stem the
tide against them. The only thing they still command in full is the art
of destroying their opponents by means of falsehood and violence. They
have shown a complete lack of understanding of the pre-requisites under
which alone Socialist production is possible, as well as entire lack of
perspicacity in determining the conditions essential for the development
of capitalist production. In their aspiration for the realization of
Socialism they have destroyed Russia’s entire machinery of production,
while their present effort to patch it up with the assistance of
capitalism carries the danger of aggravating this destruction. But even
should they succeed in establishing a new capitalism in Russia and to
resume production with its assistance, they would do so in the presence
of a proletariat which they themselves have rendered unfit for struggle
and resistance.
In both cases, misery and poverty will continue to reign in Russia
for many years and will continue to fan apathy and despair, on one side,
and uprisings, provoked by the despair of the masses – on the other.
The Moscow trial was intended to distract the growing opposition of the
masses against the Bolsheviki and direct popular wrath against the
Socialists-Revolutionists. How vain the effort! The arrow, in falling,
struck the ones who fired it.
The Bolsheviki hoped to represent the accused
Socialists-Revolutionists and their entire party as allies and
associates of the counter-revolution and foreign powers. To accomplish
this aim, they did not hesitate to employ the most shameless and
dishonest methods of the regime of the old police. They outdid the
limitless shamelessness of that regime, whose prosecutors, as is well
known, needed but a few lines penned by the accused to send him to the
gallows. With all that, however, the Bolsheviki succeeded only in
exposing the mean depths of their own soul.
When the counter-revolution suppressed Marx’s Neue Rheinische Zeitung,
in 1849, Freiligrath branded this act in words of fire as contemptible
violence. He said: “This is not an open blow in an open fight. Against
me are barbarism and meanness. This blow has been struck against me by
the forces of sneaky, dirty, despicable Asiatic barbarism”.
The defendants in the Moscow trial were likewise struck not by an
open blow in an open fight. The blow struck against them was delivered
by the hired, contemptible, low hirelings of Tartar or Kalmyk socialism.
But how innocent was the despicableness assailed by Freiligrath in
comparison with the despicableness revealed by the Bolsheviki in the
Moscow trial! The shameless falsehood, contemptible cowardice and
devilish cruelty of the prosecutors, judges and secret service men
revealed in the Moscow trial are unprecedented in the history of the
world and will mark one of its most shameful pages.
How heroic do the figures of the accused men and women appear and how
disgusting and pitiful are the pack of hounds who demanded their blood,
who hurled insult and humiliation upon them in their eagerness to
persecute them in order that they might revel in their suffering!
The moral loftiness of the accused and the moral degeneration of
their accusers at the trial were so self evident and convincing, that
the whole thing formed a picture of remarkable clarity and produced an
indelible impression upon everybody, with the exception of the pack of
bloodthirsty hounds hired by the Moscow executioners to defend their
miserable case in the European press and who were low and mean enough to
do it.
The accused Socialists-Revolutionists saved the honor of Socialism,
trampled by the Bolsheviki. The names of Gotz, Timofeyeff and their
comrades will be enshrined in the hearts of the workers of the entire
world, regardless of party affiliations.
Never did the Bolsheviki descend to their present low level. Time was
when we knew many of them as honest fighters and idealists. But the
coup d’etat of 1917 placed them in a false position, which was bound to
lead consistently to their inevitable and ever-growing perversion.
From the very beginning, they founded their power upon falsehood and
violence directed against the proletariat, upon the principle that the
end justifies the means. This principle always and inevitably leads to
the degeneration of the party applying it, for it perverts the party and
paralyzes those who do not oppose this perversion.
Parties who aspire to great aims cannot afford to use any other means
than those these aims demand. A party who seeks the emancipation of the
proletariat cannot, in its efforts to gain and hold power, use means
which disorganize and demoralize the proletariat. But it was only by
such means that the Bolsheviki could strengthen their hold upon Russia
and, therefore, they preferred the destruction of the Russian and the
weakening of the world proletariat to understanding with the other
Socialist parties of Russia, which alone could secure the establishment
of a revolutionary regime that would support itself upon the broad
masses and give these masses that freedom without which it is impossible
for them to promote their spiritual development and economic
well-being.
By resorting for the sake of the strengthening and preservation of
their power to measures leading to the weakening and dissolution of the
proletariat, the Bolsheviki have shown that they are not concerned with
the emancipation of the proletariat but are simply a clique concerning
itself solely with the preservation of its own power.
This attribute of Bolshevism makes it akin to the heritage of the
French Revolution: bonapartism. Like bonapartism, Bolshevism is founded
upon falsehood and violence. But both the first and second Empires
marked the opening of new eras of economic prosperity for France and
could, therefore, support themselves not only upon the capitalists and
peasantry but also upon the broad masses of the people. Bolshevism, on
the other hand, has destroyed Russia and set all the people against it.
Its falsehood and violence, therefore, exceed the falsehood and violence
of French bonapartism. And for this reason, despite its falsehood,
meanness and cruelty, Bolshevism will not be able to maintain itself as
long as did the regime of Bonaparte in France.
The Moscow trial constituted a desperate effort on the part of the
Bolsheviki to discredit their most dangerous opponents at the present
moment in the eyes of the Russian and world proletariat. They sought to
represent these opponents as associates of the counter-revolution and
thus rehabilitate the prestige of Communism, which has lost the
sympathies of the overwhelming majority of the proletariat.
But the Bolsheviki lost the trial. It is not the accused but the
accusers and their hirelings who today stand condemned in Russia and
throughout the world. This trial, which provoked the deepest, universal
contempt, revealed even to those who hitherto still failed to see the
truth, the utter decay and degeneration of the Bolshevist regime.
But the Moscow trial is merely one of the episodes incident to the
world-wide, historic conflict conducted by Bolshevism. Out of this
conflict it will emerge discredited and condemned. A regime like that of
the Bolsheviki has already grown rotten-ripe for destruction. It is
impossible to foresee yet when and how it will fall but one thing can be
said now and with absolute certainty:
BOLSHEVISM WILL FALL IN SHAME AND DISGRACE, BEMOANED PERHAPS ONLY BY
THE SPECULATORS OF THE CAPITALIST WORLD, BUT ACCOMPANIED BY THE CURSES
OF THE ENTIRE WORLD PROLETARIAT STRUGGLING FOR EMANCIPATION. THAT IS THE
LESSON AND THE HISTORIC SIGNIFICANCE OF THE MOSCOW TRIAL.
K. Kautsky
Τρίτη 9 Απριλίου 2019
Γεζίντι: Τα απομεινάρια μιας υπόθεσης που δεν έκλεισε..
Όταν δεν υπάρχει ακόμα κουβέντα από τούς Άραβες και Παλαιστίνιους "επαναστάτες" για την ειδική ευθύνη τού ISIS στην εξόντωση των κουρδογενών Γεζίντι, αλλά και την γενική αλλά όχι εξ΄αυτού μικρότερη ευθύνη του θεοκρατικού φονταμενταλισμού και του αραβικού και τουρκικού εθνικισμού σε αυτό το μαζικό έγκλημα, όταν η "παγκόσμια" "αντιμπεριαλιστική" αριστερά, τα κομμουνιστικά κόμματα σιωπούν, κρύβονται, και το μόνο που ξέρουν είναι να είναι όπως πάντα μόνον "αντισιωνιστές", όταν η ριζοσπαστική αριστερά (πέραν τού Σύριζα που ασχολείται με καρέκλες και διορισμούς) ή η αναρχία-αυτονομία (όταν δεν είναι χυδαία όπως η "Επιθεώρηση Σεράγεβο") προσπαθούν ακόμα και σήμερα να "συνθέσουν" τα ερείπια τής ιδεολογικής και ηθικής ενότητας των ανθρώπων και των λαών πάνω στο ρήγμα και το βάραθρο που ανοίχτηκε και από την αδιαφορία των Αράβων "επαναστατών" "αντιιμπεριαλιστών", όταν δηλαδή ψευτοπροσπαθούν να κλείσουν με εύκολες εξ' αποστάσεως και θεωρητικές μόνον ενώσεις τραύματα που δεν μπορούν πια να κλείσουν, όταν κρύβουν τα κενά αδελφικών πράξεων ή έστω σαφών διακηρύξεων και καταδικών που δεν υπήρξαν ούτε υπάρχουν, τότε το μόνο που μένει μετά από την οργή είναι η κατάπληξη, η απορία, η απόσταση, το χάσμα.
Καμία στήριξη σε κανέναν σας, καμία..
Σε κανέναν σας..
Καμία στήριξη σε κανέναν σας, καμία..
Σε κανέναν σας..
Ιωάννης Τζανάκος
Δευτέρα 1 Απριλίου 2019
Ικρίωμα
Βακχεύουν δηλητηριασμένοι
οι επιμελείς δαίμονες της αρετής
οι επιμελείς δαίμονες της αρετής
Δεν
υπάρχει Σωτηρία !
Δριμύς ο πόνος της επίγνωσης
το δοξάρι τους βαραίνει
Δριμύς ο πόνος της επίγνωσης
το δοξάρι τους βαραίνει
Κυρτώνουν τις πληγές τους
Ονομάζοντας
Χύνοντας βάλσαμα πράξεων
Ονομάζοντας
Χύνοντας βάλσαμα πράξεων
Ας γνωρίζουν πως πεθαίνουν
Ορμούν στις πηγές
να πιούν αλμυρό φως
Ορμούν στις πηγές
να πιούν αλμυρό φως
Ο Δήμιος προσεύχεται
να τελειώσει η γιορτή
αφαιρεί το δέρμα τους και
να τελειώσει η γιορτή
αφαιρεί το δέρμα τους και
Πριν συνθλίψει την καρδιά
τους
την στρέφει στο έκνομο πλήθος
κραυγάζοντας: Ο υ σ ί α !
την στρέφει στο έκνομο πλήθος
κραυγάζοντας: Ο υ σ ί α !
Ιωάννης Τζανάκος
Παρασκευή 29 Μαρτίου 2019
Δευτέρα 25 Μαρτίου 2019
Τα είδη τού μηδενός (2014-2019)
Κείμενο σε αρχική ημι-επεξεργασμένη μορφή που αποσύρθηκε.
Κρατάω τον τίτλο τής ανάρτησης, για μελλοντική χρήση.
Εγγραφή σε:
Αναρτήσεις (Atom)
